APPARATUS REQUIRED
i) A spectrometer
ii) A Spirit level
iii) A sodium lamp
(iv) An eye-piece
(v) A diffraction grating with clamping arrangement
THEORY
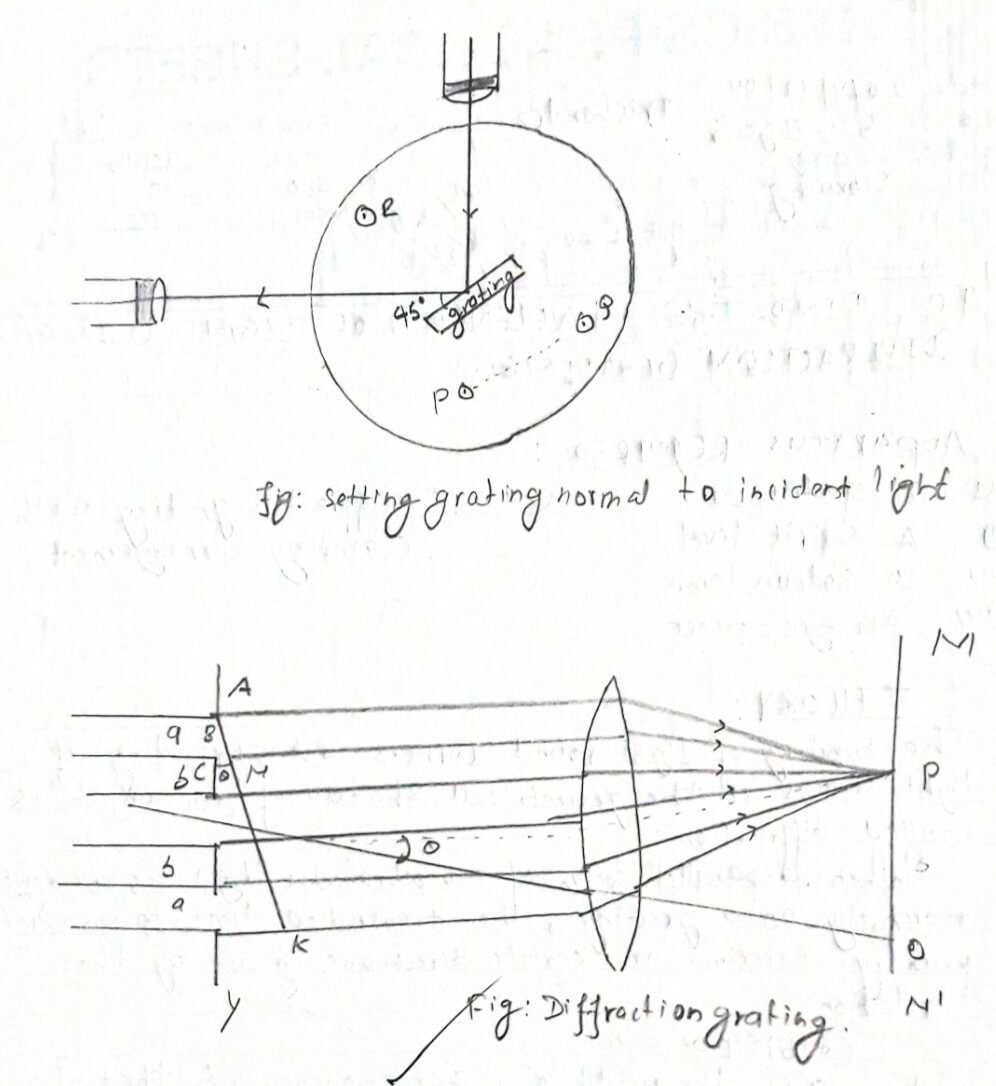
The bending of light round corners and spreading of light waves in the geometrical shadow of an object is called diffraction.
When a parallel beam of Monochromatic light is incident normally on a grating, the transmitted light gives rise to primary Maxima in certain directions given by the relation.
(a+b)sinθn = n-1
Where a is the width of a transparency, b that of an opacity, θn be the angle of diffraction for nth order maxims and λ be wavelength of light.
Therefore, λ = (a+b)sinθn /n
a = width of transparency
b = width of opacity
λ = wavelength of light
θn = angle of diffraction for nth order maxima
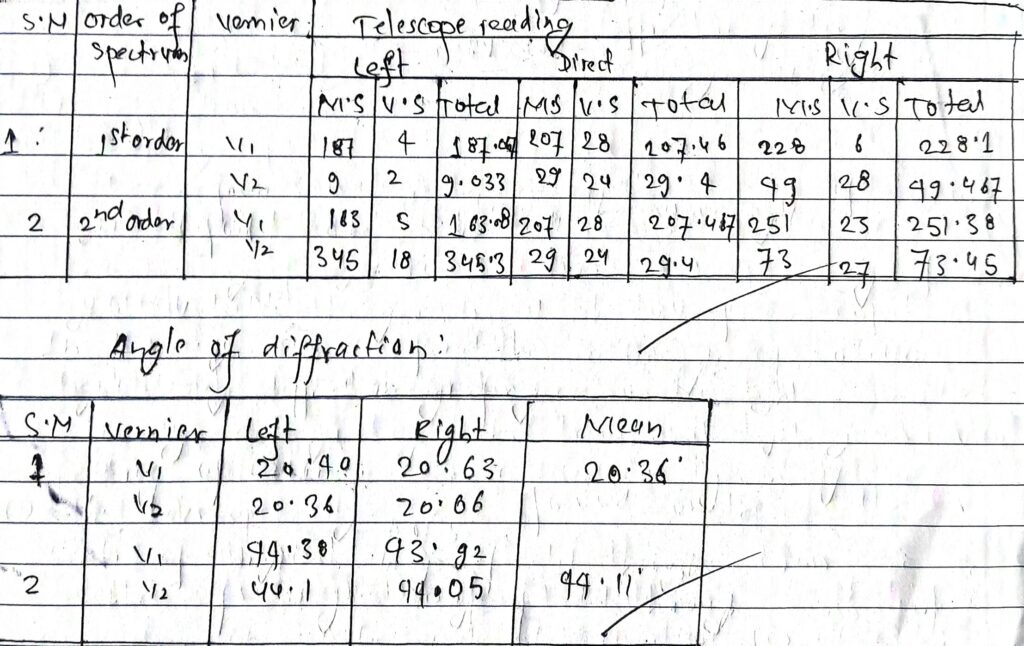
OBSERVATIONS
Vernier Constant = (1/60)
No. of lines per inch on the grating N = 15000
grating clement (a+b) = 2.54/N = 2.54/15000 cm = 1.69×10-4
Direct reading of telescope= 118.43
CALCULATION
Mean θ1 = 20.360
λ1 = (a+b)sinθ1 = 2.54/15000 x sin (20.360)
= 5.89×10-5cm
= 5.89×10-7m
Mean θ2 = 176.45/4 = 44.110
λ2 = (a+b)sinθ2/2 = 2.54x sin(44.110)/ 15000×2 = 5.89×10-7m
mean λ = λ1+λ2/2
= 5.81 x10-7m +5.89 x10-7m/2
Therefore, λ = 5.89 x10-7m
RESULT
Hence, from above calculation; the wavelength of Sodium light is found to be 5.89 x10-7m.
CONCLUSION
In this way, we can find the wavelength of sodium light using diffraction grating.
Sources of Error
i) The telescope May not be focused on the Middle or center of the brightest image of slit ii) Reading on the device might be slightly different than a dual.
iii) Carelessness of experiment on leveling the spectrometer correctly.
PRECAUTION
i) level the spectrometer horizontally.
ii) Note the reading carefully.
iii) Use a good condition spectrometer which can easily rotate the telescope.
iv) Do the experiment in absence of external light.