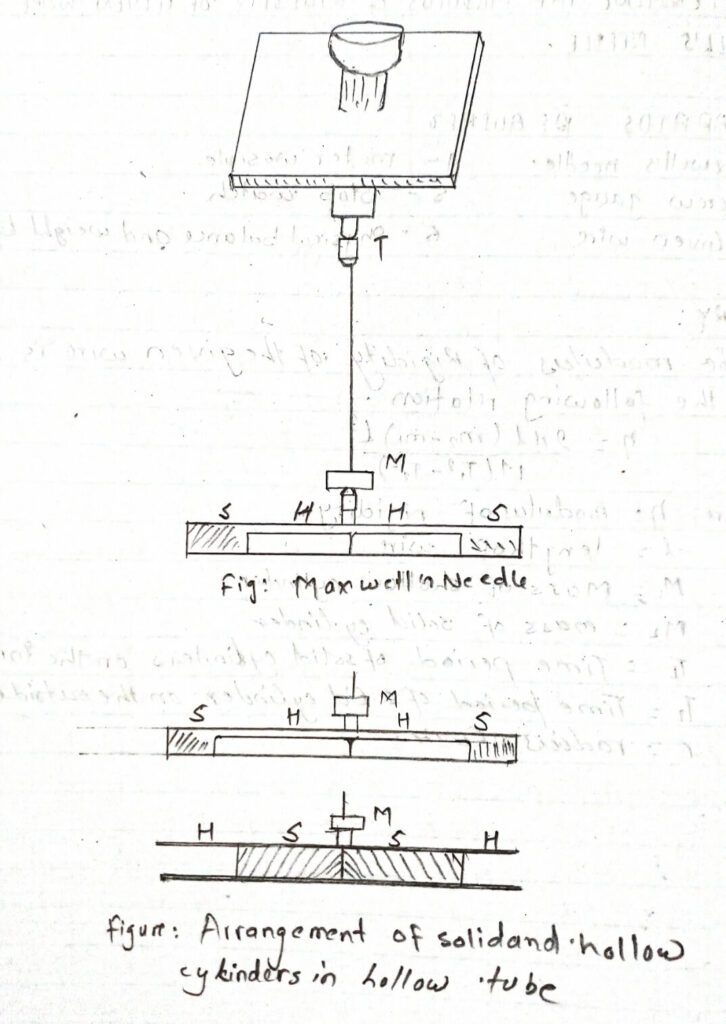
APPARATUS REQUIRED
i) Maxwell’s needle.
ii) Screw gauge
iii) Meter scale
iv) Stopwatch
v) Given wire
vi) Physical balance and weight box.
THEORY:
The modulus of Rigidity of the given wire is calculated by the following relation.
η = 2πl(m2-m1) l3 / r4(T21-T22)
Where, η = modulus of rigidity.
l= length of wire
M1 = Mass of hollow cylinder
M2 = mass of solid cylinder
T1 = Time period of solid cylinders on the innerside
T2 = Time period of solid cylinder on the outside
r= radius of wire
OBSERVATION:
Table for determination of T1 and T2
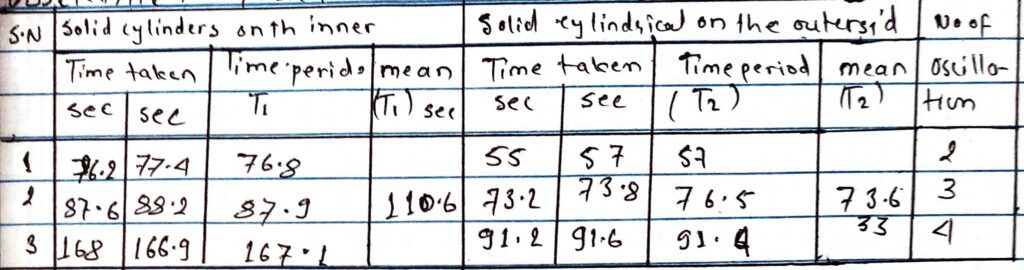
length of wire (l) =79cm =0.79m
length of maxwell’s needle (l) = (0.41) m
Mass of hollow cylinder (M1) = 50 gm = 0.05kg
Mass of solid cylinder (M2) = 250gm = 0.25kg
Radius of wire (r) = 45×10-5/2 m
CALCULATION
Modulus of rigidity (η) : 2π(m2-m1)l2 / r4(T21-T22)
= 2π(0.25 -0.05) (0.41)2 / (45X10-5/2)4 [(110.6)2-(73.633)2]
= 9.40×109 N/m²
PERCENTAGE ERROR
Standard value 7η = 1.7 × 1011 N/m2
observative value (η) = 9.4×109 N/m²
Here error = Standard value-observative value / Standard value X100%
= 94.5%
RESULT:
Thus the modulus of rigidity of the given wire was found to be 1.40X 109 N/m2
CONCLUSION
Thus the modulus of rigidity of the given wire can be determined by using Maxwell’s needle.