COMMENTS ON ALBUGO
Obligate parasite
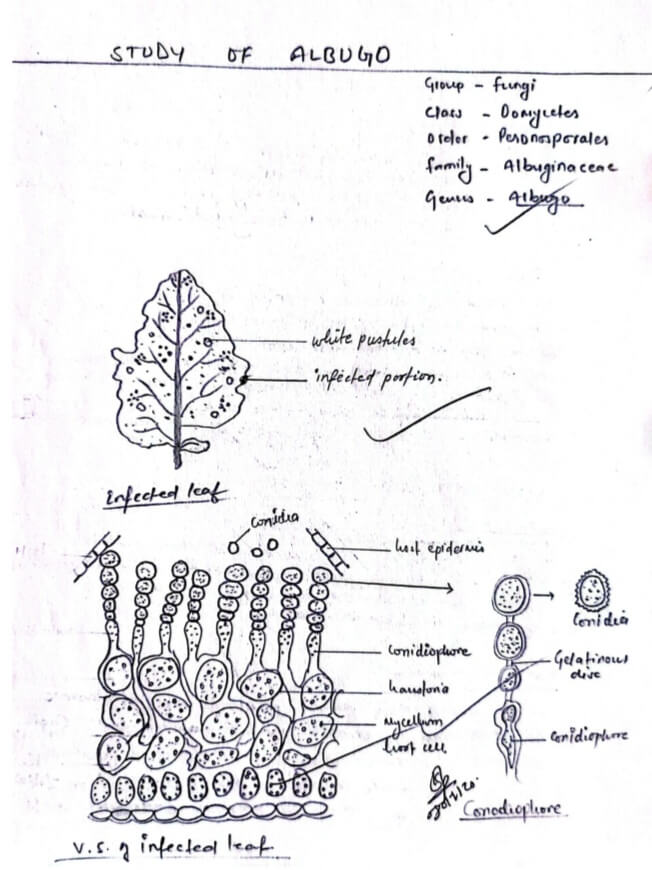
Albugo is an obligate parasite in the aerial part of Cruciferous plants such as radish, mustard, cabbage etc. The infected part is recognized by white powdery pustules on the surface of infected parts, thus named as white rust.
Somatic structure
The somatic structure is composed of simple endo- parasitic branched coenocytic hyphae. The mycelium is intercellular lying beneath the host epidermal layer. It has a knob-shaped absorbing organ called haustoria here and there. The protoplasm of a septate hyphae contains a large number of nuclei distributed in cytoplasmic mass surrounding many vacuoles, oil drops and glycogenosis reserved food bodies.
Asexual reproductive structures
i) Basipetal succession conidiophores:
The conidiophores are erect clubs-shaped, thick walled, multinucleate structures developed from the sub- epidermal mycelium. The conidia are borne in the chain of tip of conidiophores in basipetal succession.
ii) Creamy Mass Conidia:
They are round thin walled multinucleate cytoplasmic masses surrounded by smooth double layered walls. Each conidium is separated from each other by a gelatinous disc. The Creamy white conidia powder exposes the surface of the infected portion by breaking the epidermal wall.