APPARATUS REQUIRED
i) Beater
ii) Filter stand
iii) Funnel
iv) Filter Paper
v) Test tube
vi) Burner, tripod stand and wire gauge
CHEMICAL REQUIRED
i) Mixture of sand and CaCO3
ii) BaCl₂ solution.
iii) Dil HCL
iv)Na2CO₂ solution
v) AgNO3 solution.
THEORY
Sand and calcium carbonate are soluble in water. So, dilute hydrochloric acid is taken as solvent because calcium carbonate is soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid. The mixture is filtered and is obtained as residue with sodium carbonate solution to recover calcium carbonate.
Heterogeneous mixture:
The mixture in which the mixing component can be seen by our naked eye is known as heterogeneous mixture.
Precipitation reaction:
The double decomposition reaction usually between two solution resulting in the formation of an insoluble substance is known as precipitation reaction.
Precipitate:
The insoluble solid which is obtained during precipitation reaction is known as precipitate.
Filtration:
The process of separating the insoluble component from the solution of the soluble component with the help of filter paper is known as filtration.
Filtrate:
The clear liquid which is left after filtrate is known as filtrate.
dil. 2 HCL
Sand + CaCO3 —————————–>Sand + CaCl2 + CO₂ + H₂O
(S) (aq) (g)
CaCl2 + Na2CO3 —————————-> CaCO3 + 2NaCl
(aq.) (aq.) (s) (aq)
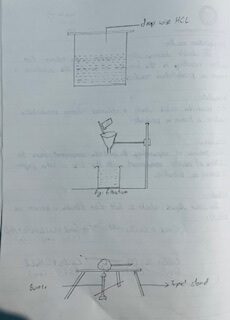
PROCEDURE
Above 2 gram of mixture of sand and calcium carbonate was taken in a small beaker and dropwise dil. HCL solution was added fill the complete appearances of CO₂ ceases. The solution was filtered. The sand was washed 3-4 times with water to remove chloride ion the sodium carbonate solution was added to the filtrated till the white ppt of calcium carbonate was obtained. The ppt of calcium carbonate was obtained. The ppt of calcium carbonate is filtered and washed with water. The purity of the solution was tested by BaCl2 solution. The ppt of C₂CO3 and sand was dyed over burner and submitted to the teacher.
OBSERVATION TABLE
| S.N. | Experiment | Observation | Inference |
| 1. | Sand washed water was tested with AgNO3 solution. | Curdy white ppt was observed. | Presence of Cl– . |
| 2. | After washing the sound sand water was treated with an AgNO3 solution. | No ppt was observed. | Absence of Cl– . |
| 3. | CaCO3ppt washed water was treated with AgNO3 solution . | White ppt was observed. | Presence of Cl– . |
| 4. | After washing CaCO3 ppt washed water was treated with AgNO3 solution. | No any ppt was observed. | Absence of Cl– . |
| 5. | CaCO3 ppt washed water was treated with BaCl2 solution. | White ppt was observed. | Presence of soluble CO3 – |
| 6 | After wasting, CaCO3 ppt washed water was treated with BaCl2 solution. | No any ppt was observed . | Absence of soluble CO3 – |
TEST REACTION
AgNO3 + Cl– —————-> AgCl ↓ + NO3—
(Curdy white ppt)
BaCl2 + CO3– ————–> BaCO3 + 2Cl–
(white ppt)
RESULT
Pure sand and pore CaCO3 were separated from the mixture by precipitation, filtration and drying.
CONCLUSTON
The two water insoluble components can be separated by dissolving dilute HCl by precipitation.
PRECAUTION
i) All the apparatus should be handled carefully.
ii) Dilute H₂SO4 should not be used since insoluble CaSO4 coils are formed.
iii) The precipitation of CaCO3 should be complete.
