THEORY:
Distillation is the process of converting a liquid into its vapour by the application of heat, and then condensing the vapour into the same liquid by cooling.
That is, vaporization + condensation makes distillation. Hence the process of distillation can be employed to recover a solvent from a solution containing dissolved solids.
APPARATUS :
1) Distilling flask
2) Liebig’s condenser
3) Conical flask
4) Rubber tubing
5) Stand and clamps
6) Water trough
7) Clock glass
8) Beaker
9) Tripod stand and wire gauze.
CHEMICALS:
1) Impure water containing some NaCl, CuSO4 etc.
PROCEDURE:
A. Tests for dissolved solids
Perform the detection and the tests for the dissolved solids as follows.
| Experiment | Observation | Inference |
| i) Evaporate a little of thegiven sample on a clockglass kept over a beakerhalf filled with water | Solid residue left on theclock glass | Presence of dissolvedsolids |
| ii) A little sample + 2 dropsAgNO3 | Curdy white ppt White ppt | Presence of chloride |
| iii) A little sample + 2 dropsBaCl2 | White ppt | Presence of solublecarbonates or sulphates. |
| iv) Test the sample withblue and red litmus | i) turns blue litmus red.ii) turns red litmus blue | i) acidic impuritiesii) basic impurities |
B. Distillation
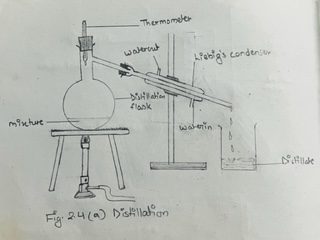
a. Assemble the apparatus as shown in the figure 2.4 (a)
b.Take the given solution in the distilling flask, and heat it over the wire gauze by means of the Bunsen flame till it boils. The solvent vaporized, and is gradually condensed back to the liquid state as it passes through the Liebig’s condenser which is kept cool by the circulation of water. The condensed liquid trickles down, and is collected inside the receiver. The pure liquid thus collected in the receiver is called the distillate.
c.Use the first portion of the distillate to wash the receiver, and reject it into the sink.
d. Collect the subsequent portions of the distillate, and repeat the above tests with small samples of the distillate.
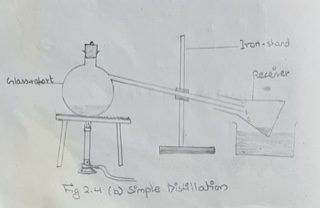
N.B. In case, the distilling flask and condenser are not available, a glass retort as shown in fig. 2.4 (b).
Or
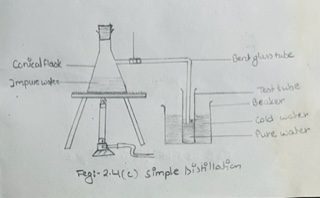
A conical flask with a side tube as shown in fig 2.4 (c) may be used for simple distillation.
Tests for the Purity of the Distillate:
| Experiment | Observation | Inference |
| i) Evaporate some distillate on a clock glass as before | No solid residue | Absence of dissolved solids |
| ii) A little sample + 2 drops of AgNO3 | No ppt | Absence of chloride |
| iii) A little sample + 2 drops of BaCl₂ | No ppt | Absence of soluble carbonates or sulphates |
| iv) Test the distillate withblue and red litmus | No effect on thelitmus papers. | The distillate is neutral. |
Separation of Two Immiscible Liquids
