APPARATUS REQUIRED
i) A NPN Transistor
ii) Batteries
iii) A voltmeter
iv) Connecting wires
v) Potentiometer
THEORY
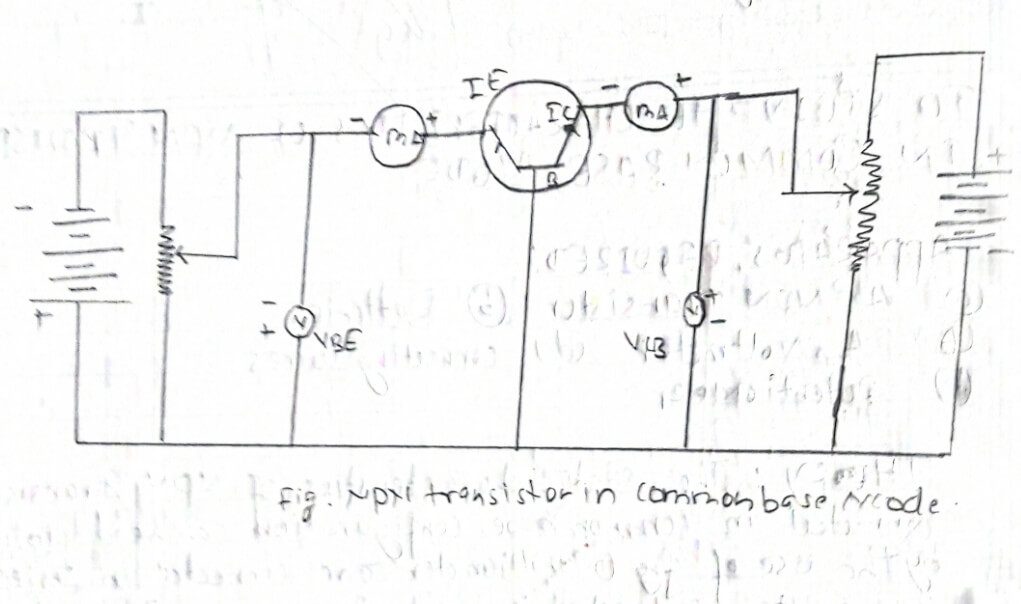
The static characteristics of NPN transistors connected in common base configuration can be determined by the use of fig (i) millicenters connected in series with the emitter and collector or units to measure IE and IC. Similarly voltmeters are connected across the emitter and base to measure voltage VBE and cross collector and base to measure VCB. The two potertiometer from the collector and the emitter dc supply.
(i) Input characteristics :
The relation between Ie and Veb at constant value at the collector voltage. These are known as input characteristics.
(ii) Output characteristics:
The relation between Ie and Veb at constant valves of emitter cement. This is known as output characteristics.
Transfer characteristics:
The relation between Ic and Ie col constant collector base voltage shows the transfer characteristics.
OBSERVATION
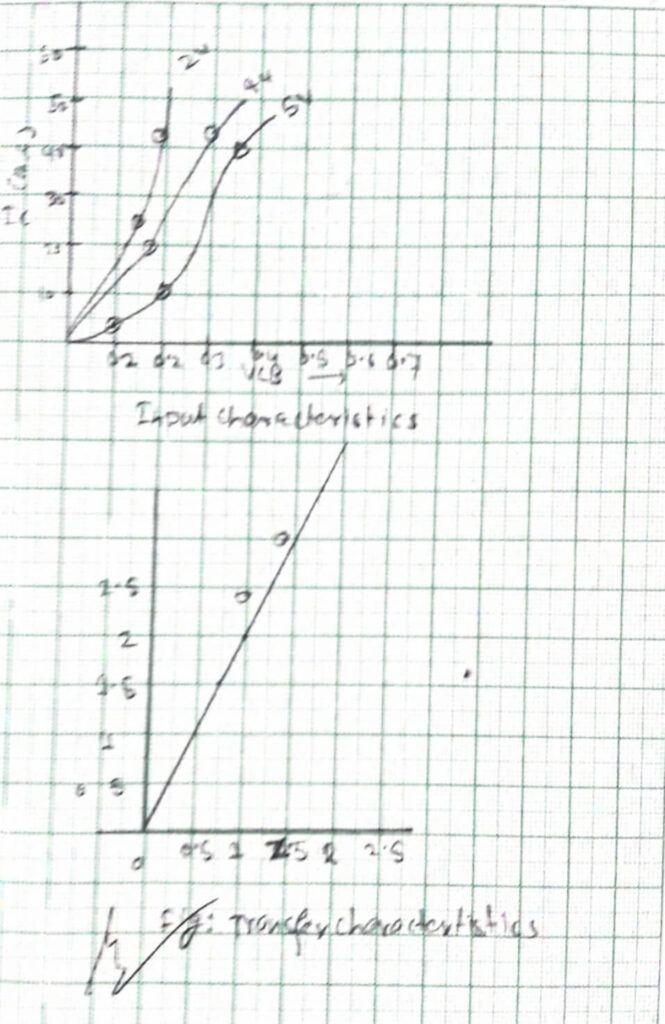
1) INPUT, CHARACTERISTICS
| S.N | VBE | IE(MA)/VCB=2V | VCB=4V | VCB=5V |
| 1 | 0.1 | 11 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 0.2 | 11 | 15 | 16 |
| 3 | 0.24 | 40 | 50 | 55 |
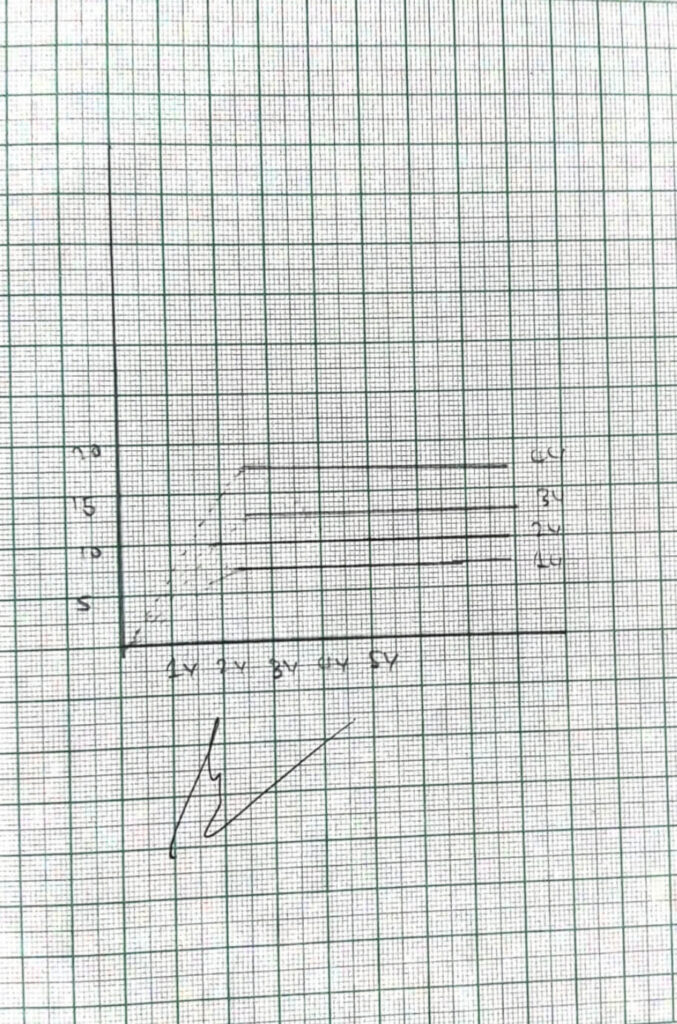
2) OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
| VCB | IE= 8MA | IE= 9mA | IE= 7MA |
| 1 | 7.8 | 8.4 | 6.5 |
| 8 | 8.6 | 6.6 | |
| 8 | 8.6 | 6.6 | |
| 8 | 8.6 | 6.6 |
3) TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS
| IE | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| IC | 0.8 | 1.8 | 2.8 |
RESULT
Hence, the NPN transistor in common base mode is verified.
CONCLUSION
INPUT, OUTPUT and transfer characteristics are used to verify transistors in common base.
PRECAUTION
i) Collector voltage must not exceed breakdown voltage.
ii) Correct value of blasing potential must be employed.
iii) NPN transistor emitter must be given a positive potential with respect to base