APPARATUS REQUIRED
i) Traveling microscope
ii) Three capillary tubes of different diameters
iii) Beaker
iv) Index Rod
v) Clamp
vi) Stand
THEORY
Surface tension is force per unit length acting on either of an imaginary line the liquid surface in equilibrium. The direction of force is tangential to the surface and perpendicular to the line.
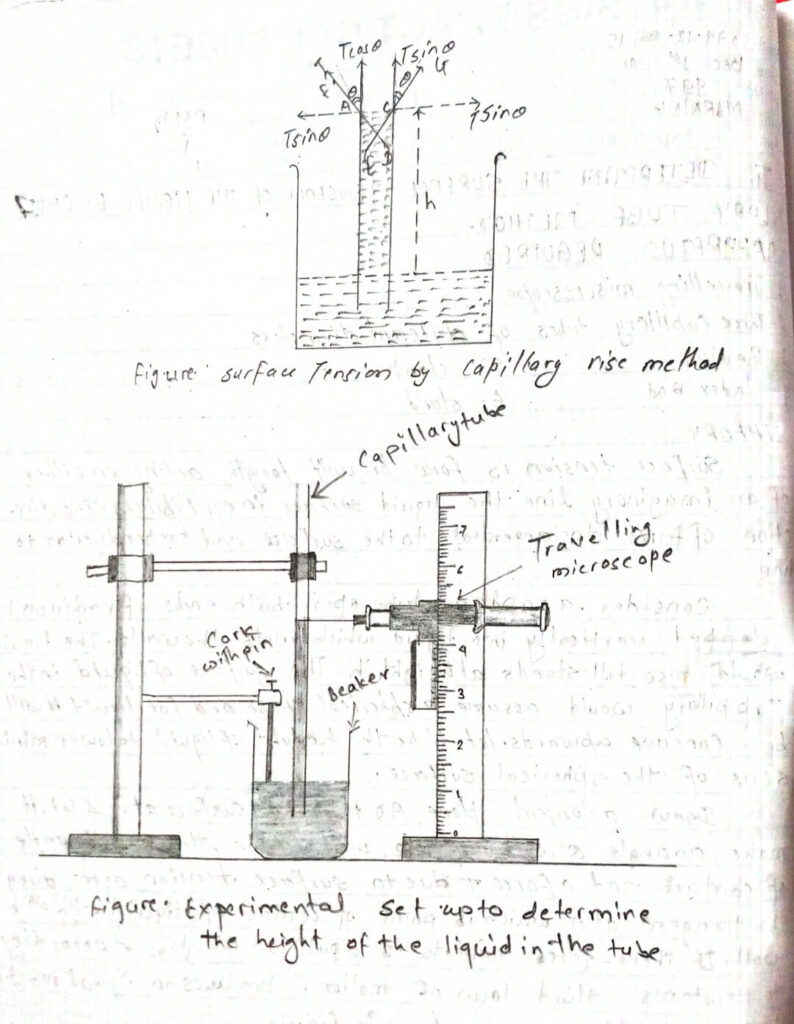
Consider. a capillary tube opens both ends of radius (r) deped vertically into liquid which wets the walls. The liquids would rise till they stand at height (h). The surface of liquid in the Capillary would assume a spherical shape and for liquid iI will be concave upwards. let. (h) be the height of liquid to lower the meniscus of the spherical surface.
Draw a tangent plane AD to the liquid surface at A and let it make an angle θ with the vertical wall of the tube, then θ is the angle of contact and a force T due to surface tension acts along the tangent at A which is the point of contact of liquid with the wall. If there-force expert is a pull on the glass and according to Newton’s third law of motion, produces an equal reaction in the direction AF as shown in figure.
The component of this reaction in the vertically upward direction is Tcasθ and the horizontal direction is Tsinθ · Since the liquid surface in tubes makes a circle of contact with the walls of the tube, the horizontal components acting in one half of the circumference are equal and opposite to those acting in the other half of the circumference and hence their effect is zero. The Total vertical component of the force acting in upward direction is equal to 2πrXTcasθ, where, (r) is radius of the circular tube. This force is responsible to pull liquid in upward direction and the liquid continues to rise till the force is balanced by the upwards force due to the weight of the liquid inside the capillary tube above the surface of the liquid in the beaker.
If the capillary is sufficiently harrow, then the meniscus is hemispherical and has the same radius as that of the tube, If 𝛿 is the density of the liquid. then,
Total weight of liquid column = mg = volume x density x g.
= πr²h + r/3𝛿g
In equilibrium position
2πr.T Cosθ = πr²h + r/3𝛿g
Surface tension of the liquid, T = h + r/3𝛿g/2Cosθ
Since, r/3 is very small on comparing with h for small capillary tube, T= rh𝛿g/2Cosθ
We know, For clean water and glass, angle of contact θ=0
i.e. Cosθ =1 therefore, T= rh𝛿g/2
PROCEDURE
i) Take three capillary tubes of different diameter, fix them vertically on the glass plate the of wax or sticky substance.
ii) The glass plate stuck with the capillary tube and needle is lowered. The lower end of the tube is inside the water of the needle and just touches the water substance in the beaker.
iii) Do the same for capillary tubes also.
iv) Focus the microscope on the lower tip of the needle.
v) Focus the microscope on the lower meniscus of water in the tube.
OBSERVATION
Value of 50 Vernier scale division = 49 msd
value of 1 vernier scale division = 49/50
Vernier constant = ( msd – 49/50) = 0.01m.m = 0.01/100 = 0.001
V.C = 0.01 mm = 0.001 cm
1 Height of liquid in capillary tube (cm)
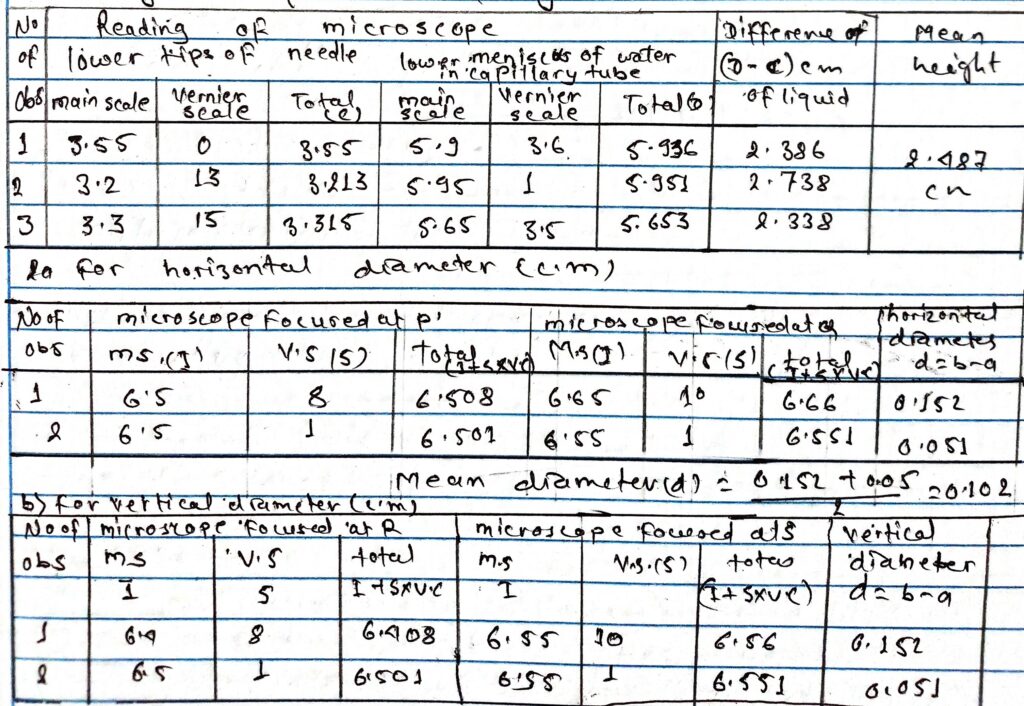
Mean diameter(d) = 0.152 +0.051/2
=0.102
CALCULATION
Radizco of tube(r) = a/2 =0.051cm
Height of liquid (h) = 2.487cm
Density of water (ρ) = 1gm/cm3
acceleration due to gravity (g) = 980 cm/sec2
Then, Surface tension of water (T) = Hρrg/2
=1/2(2.487x1x0.051×980) = 62.15dye/cm
ERROR PERCENTAGE
% = tact-tobs/tact x100%
= 72.15-62.15/72.15 x100%
= 13.86
RESULT
The surface tension of water is calculated to be 62.15dye/cm.
CONCLUSION
Hence the surface tension of water can be calculated by the capillary rise method.
PRECAUTION
i) The meniscus reading should be taken carefully.
ii) Apparatus should be handled carefully.
iii) The tube should be having diameter lying between 0.5 & 1.5 cm
iv) Water should rise Freely in the tube.
v) The tube should be vertical and sufficiently away from the needle.
vi) Do Not use wax for fixing the tube in the glass-plate.
vii) The surface of water should not be touched by hand.
viii) The tip of the needle should just touch the water and not dip into it.