EXPERIMENTAL LOCATION
Local grassland
THEORY
The grassland is an open terrestrial community covered with grasses. It has varieties of organisms that are interacting together as well as they interact with their physical environment. All the food chains are interconnected and overlapping within an ecosystem and they make up a food web.
Food web describes how life’s energy flows through the gramland.
i) Producer level
Producers are able to capture the sun’s energy through photosynthesis and absorb nutrients from the soil, storing them for the future. Grasses, shrubs, trees, roses, lichens and cyanobacteria are some producers found in grassland and ecosystem.
ii) Consumers
Consumers are organisms that do not have the ability to capture the energy produced by the sun but consume plant and animal material to gain their energy for growth and activity.
iii) Decomposers
Decomposers include insects, fungi and bacteria both on the ground and soil that help to break down organic layers to provide nutrients for growing plants.
Plant → Grasshopper → frog → Snake → Hawk
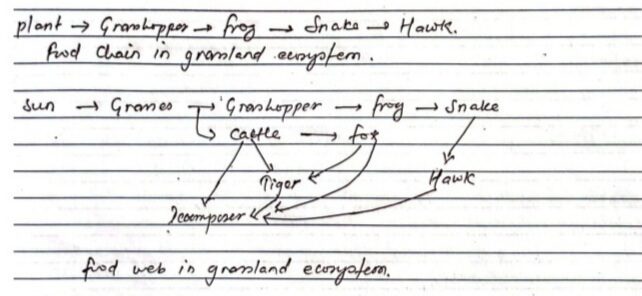
food chain in the grassland ecosystem.
RESULT
Note all the possible food web in biotic facts like prodcer primary, secondary and tertiary consumer as studies in experimental gramland.