EXPERIMENTAL LOCATION
Local pond
THEORY
In an ecosystem one organism does not depend wholly on another. The Monh plants are eaten by a variety of insects, birds, Mammals and fishes. Some of the animals are eaten by sereral predators. All the food chains are interconnected and overlapping within an ecosystem and they make up the food web. Food web describes how life energy flows through the pond.
i) Producer level
Producer level of pond food web collectively includes many species of floating and rooted aquatic plant life that absorbs there such as sunlight, water, air and soil materials. Produces include microscopic, floating plant life collectively known as algae and larger rooted water plants.
ii) Primary consumer
It consists of tiny herbivorous animals that feed on algae and other aquatic plants to sustain themselves. These animals include insèch, tadpoles, very small fish and snails. There are variety of microscopic animal burns as zooplanktons
iii) Secondary Consumer
They eat primary consumers. The second level of animal consumer includes many species of fish, frogs, other crayfish and reptiles.
iv) Tertiary Consumer
They eat both primary and secondary Consumers. It includes fish and frog eating water birds, fish eating hawks, etc.
v) Decomposer
Bacterio, fungi and insect/animal scavengers, complete the pond food web, breaking down dead and decaying aquatic plant and animals.
Producer Primary Consumer → Secondary Consumer→Tertiary Consumer
Sun → Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Small fish → large fish → Decomposers
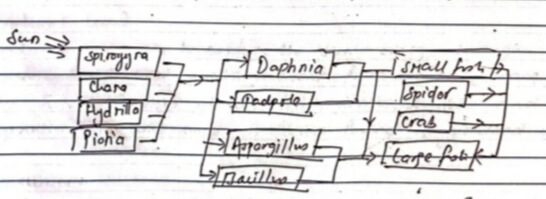
Food web in pond ecosystem.
RESULT
Note all the possible total food web in biotic factor live producer, primary, secondary, and tertiary Consumers as studied in the experimental pond.