COMMENT ON CHARA
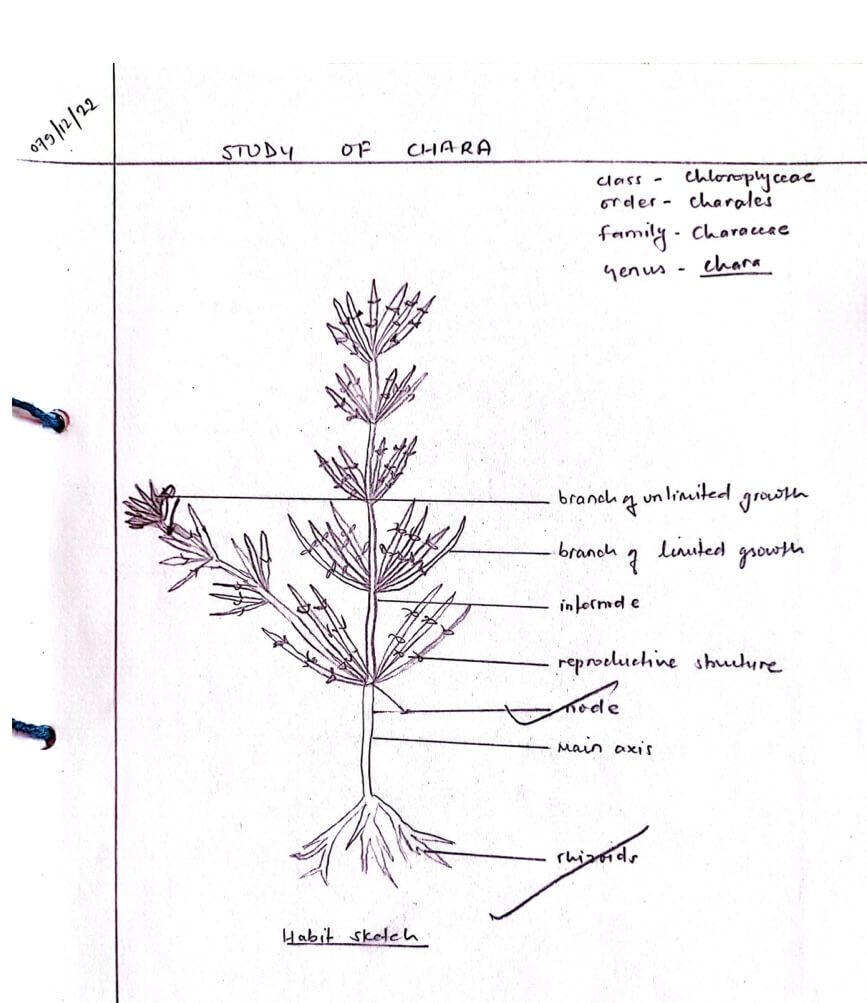
Habit
Chara is a submerged plant growing in the muddy or sandy bottom of pools and ponds of clear and hard water. It gets attached to substratum by the rhizoids.
Vegetative Structure
Elongated algae:
It is a profusely branched algae. The main axis is differentiated into rhizoids, stem and leaves. The elongated axis is divided into nodes and internodes.
The base of each node is furnished with a number of unicellular spine-like outgrowths called stipulodes.
Dimorphic branch:
The nodes give rise to whorls of small green elongated leaves with nodes and internodes.
Vegetative Reproductive Structure
Amylum or starch stars:
They are star-shaped amylum, starch rich cells developed under the lower nodes of the main axis. It grows in a new plant after detachment from the mother plant.
Tuber or bulbils:
They are starch rich swollen tuber or bulbil- like outgrowth originated from some rhizoids or burried nodes.
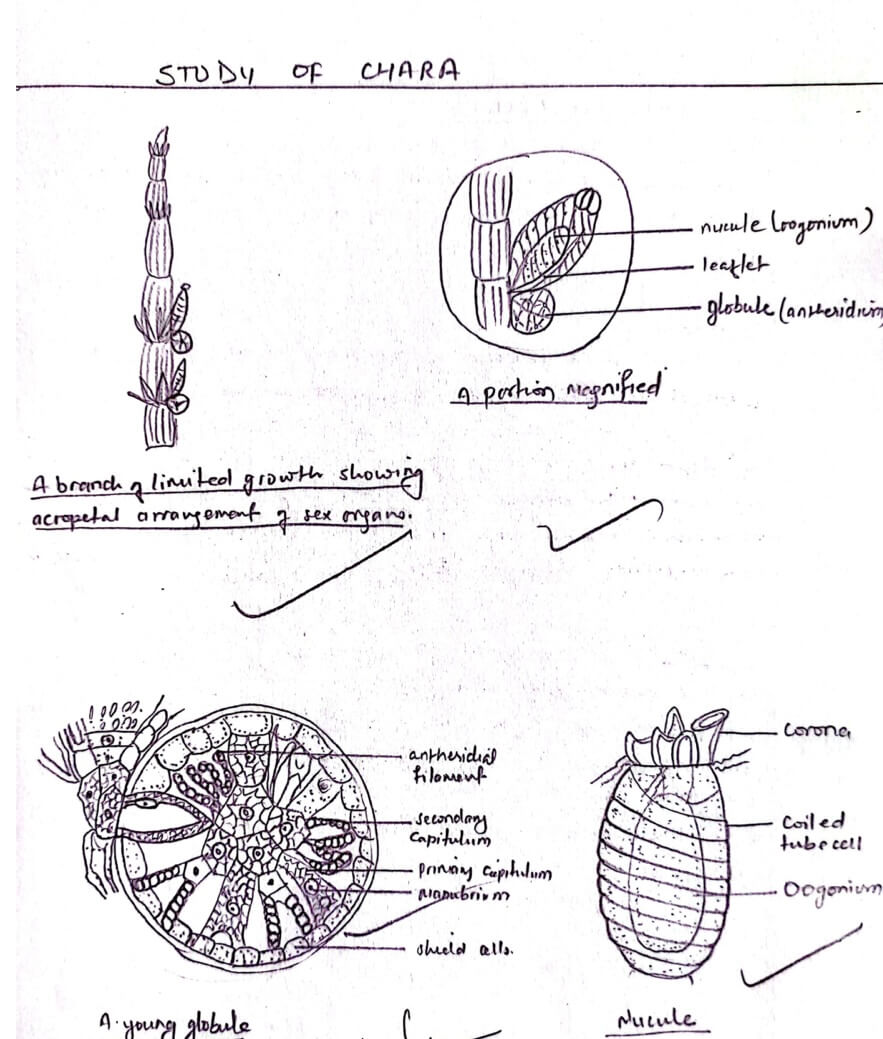
Sexual Reproductive Structure.
Oogamous :
The sexual reproduction is oogamous and carried out by special type of antheridium called globule and oogonium called nucule. They remain just apored in the same node carrying nucule above the globule.
Globule:
It is a spherical yellowish red structure comprising of eight outer shield cells. The center of each shield cell produces rod-like outgrowth called Manubrium bearing at its tip eight primary capitulum cells and many secondary capitulum cells. Each secondary capitulum cell produces two or four long whip-like segmented antheridial filaments. Each filament is composed of 100-200 segments each enclosing elongated, coiled and biflagellate antherozoids.
Nucule:
It is a shortly stalked, oral structure comprising of five spirally coiled elongated tube cells terminating into fine erect coronal cells. It encloses an uninucleate, elongated oogonium with large oral ovum or egg cells or cosphere at the basal part above the filamental cell. A clear receptive spot is at its apex.