APPARATUS REQUIRED:
- Measuring Cylinder
2. Mortar
3. Pestle
CHEMICALS REQUIRED:
Calcium Carbonate, Bentonite, Carboxymethylcellulose(CMC), Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC)
THEORY:
i) Suspension:
Suspension is a two-phase system consisting of freely divided solid particles dispersed in liquid (solid drug in liquid vehicle). The insoluble solid drug is uniformly suspended throughout the suspending vehicle (dispersion medium) by the aid of a single combination of suspending agents.
ii) Suspending agents:
suspending agents are the substances which are added to a suspension to increase the viscosity of the continuous phase so that the particle remain suspended for a sufficiently long time. Same list of suspending agents are methylcellulose, hydroxy methyl cellulase, carboxymethyl cellulose, Hydroxymethyl cellulose, Bentonite, etc.
iii) Sedimentation volume (SV).
Sedimentation volume (SV) measures how well particles settle in a suspension. It is the ratio of settled solids volume (Vs) to the initial suspension volume (Vo)
Formula,
SV= Vs/Vo
Higher SV indicates better settling while lower SV indicates poor settling. The sedimentation volume (SV) is an indicator of the physical stability of the suspension. A higher SV value indicated better stability.
PROCEDURE:
5% w/v (or 5gml) of calcium carbonate suspension was weighed in 3 each butter paper. 1% i.e. 1 gm of a different suspending agents such as bentonite, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose & hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) respectively were taken in a different vessel and added a small quantity of water and saturated well. After the powder was uniformly suspended, transferred the suspension into a separate 100ml measuring cylinder. The volume was made up to 100 ml with distilled water. The suspensions were shaken simultaneously & kept aside. Note the volume of sediment at time periods of a,10, 20, 30……..60 minutes to calculate the sedimentation volume.
OBSERVATION:
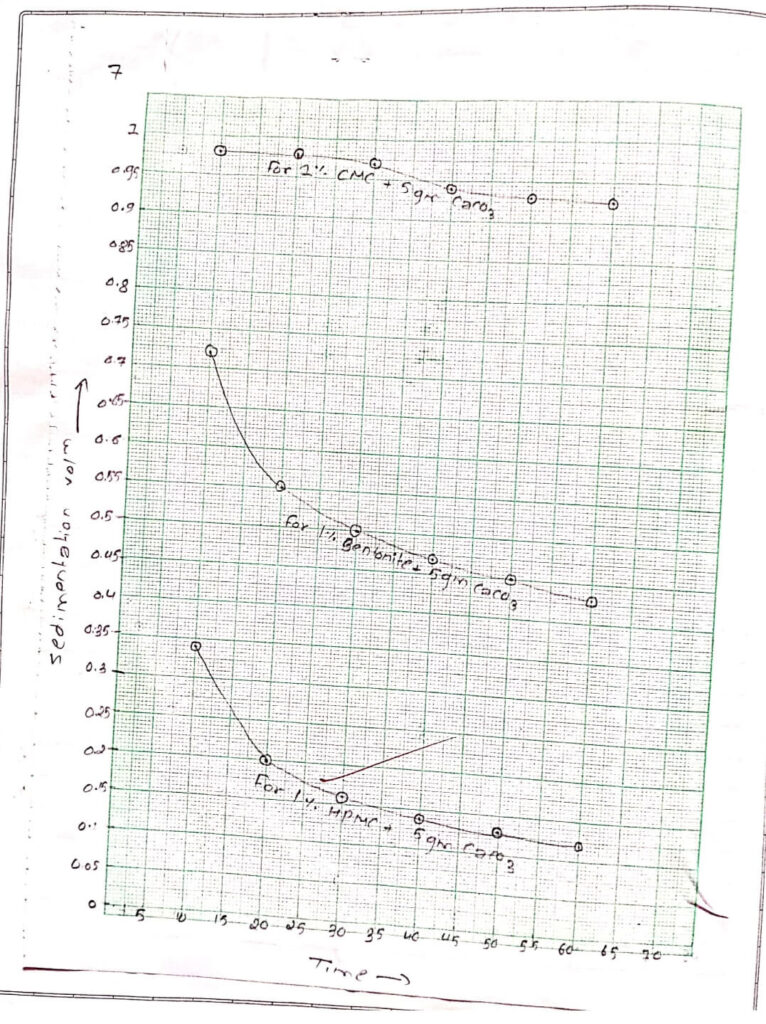
| S.N. | 1% Bentonite+ 5% CaCO3 | 1% sod, carboxymethyl cellulose + 5% CaCO3 | 1% HPMC + 5% CaCO3 | ||||||
| Vs | Vo | SV | Vs | Vo | SV | Vs | Vo | SV | |
| 10min | 98ml | 100ml | 0.98 | 72ml | 100ml | 0.72 | 34ml | 100ml | 0.34 |
| 20min | 98ml | 100ml | 0.98 | 55ml | 100ml | 0.55 | 20ml | 100ml | 0.20 |
| 30min | 97ml | 100ml | 0.97 | 50ml | 100ml | 0.50 | 16ml | 100ml | 0.16 |
| 40min | 94ml | 100ml | 0.94 | 47ml | 100ml | 0.47 | 14ml | 100ml | 0.14 |
| 50min | 93ml | 100ml | 0.93 | 45ml | 100ml | 0.45 | 13ml | 100ml | 0.13 |
| 60min | 92.5ml | 100ml | 0.25 | 43ml | 100ml | 0.43 | 12ml | 100ml | 0.12 |
A graph is plotted to observe stability of suspension putting sedimentation volume in Y-axis and time in X-axis.
RESULT:
The suspension with 1% suspending agent sodium carboxymethyl cellulose exhibits the highest sedimentation volume indicating good suspension compared in others.
More From Physical Pharmacy | 1st Year |
- Verify Lambert’s Beer’s Law & Determine KMnO4 Concentration
- To Determine Sedimentation Volume of Suspensions with Various Agents
- Sedimentation Volume: Effect of Bentonite Concentrations
- TO DETERMINE THE SURFACE TENSION OF A LIQUID (LIQUID PARAFFIN) USING STALAGMOMETER BY DROP WEIGHT METHOD AT ROOM TEMPERATURE
- Determine Solubility of Barium Chloride in Water
- Determine Bulk Density of Starch Powder: Formula & Method
- TO DETERMINE THE FLOW PROPERTY OF SUCROSE BY ANGLE OF REPOSE BY FIXED FUNNEL METHOD.
- Surface Tension of Liquid Paraffin: Drop Number Method
- Determine Specific Gravity of Glycerol Using Pycnometer
- Determine Benzene Viscosity Room Temp By OSTWALD’S U-TUBE VISCOMETER.