THEORY:
Antibiotic: A medicine (such as penicillin or its derivatives) that inhibits the growth or destroys microorganisms. The introduction of various antimicrobials for treating,variety of infections showed the necessity of performing antimicrobial susceptibility testing, as a routine procedure in all microbiology Laboratories. In Laboratories it can be made available by using antibiotic disk which will diffuse slowly into the medium where the suspected organism is grown.
The basic principle of antibiotic susceptibility testing has been used in microbiology labs for over 80 years. Various chemical agents such as antiseptics, disinfectants and antibiotics are employed to combat the microbial growth. Among those antibiotics are generally defined as the substances produced by the mos such as penicillium, which has the ability to kill or inhibit the growth of other microorganisms, mainly bacteria. Antimicrobial susceptibility tests (ASTS) basically measure the ability of an antibiotic or other antimicrobial agent to inhibit the in vitro microbial growth.
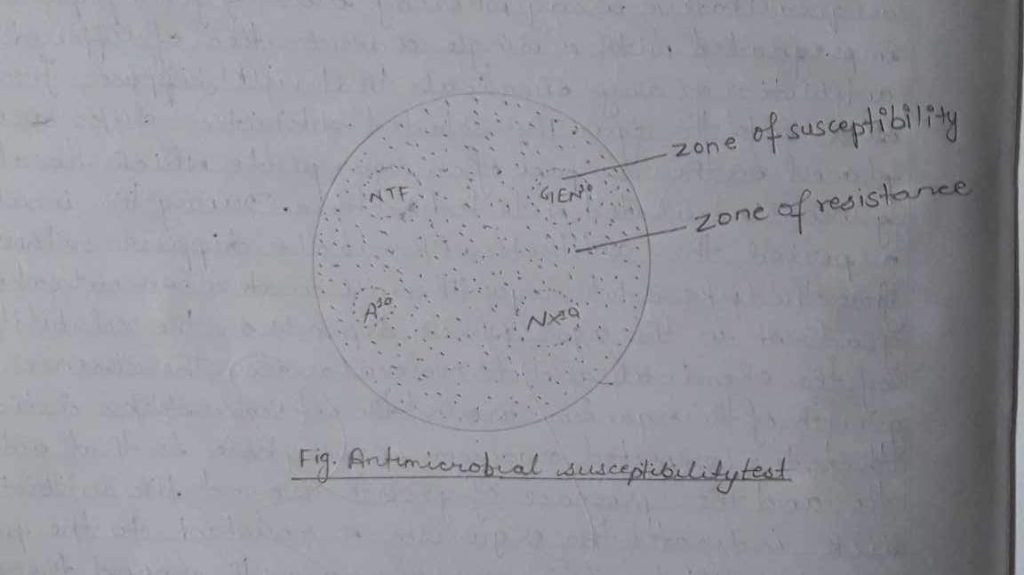
There are many different procedures that microbiologists use to study the effects of various antimicrobial agents in treating an infection caused by different microorganisms. Mueller Histon Agar (MHR) is considered as best for the routine susceptibility testing since it has batch to batch reproducibility, low conc. of inhibitors of sulfonamides trimethoprim and tetracycline and produce satisfactory results for most of the non fastidious pathogens. Fastidious organisms which require specific growth supplements need different media to grow or studying the susceptibility patterns. The Kirby Bauer test is a qualitative assay whereby discs of filter paper are impregnated with a single concentration of different antibiotics or any chemicals that will diffuse from the disk into the agar. The selected antibiotic disks are placed on the surface of an agar plate which has already been inoculated with test bacteria. During the incubation period the antibiotics, Chemicals diffuse outward from the disks into the agar. This will create a concentration gradient which depends on the solubility of the chemical and its molecular size. The absence of growth of the organism around the antibiotic disks indicates that the respected organism is susceptible to that antibiotic and the presence of growth around the antibiotic disk indicates the organism is resistant to the particular antibiotic. This area of no growth around the disk is known as zone of inhibition, which is uniformly circular with a confluent lawn of growth in the media.
The diameters of the zone of inhibition are measured (including disk) using a metric scale or a sliding calliper. The measured zone diameter can be compared with a standard chart for obtaining the susceptible and resistant Values. There are zone of intermediate resistance which means that the antibiotic may not be sufficient enough to eradicate the organism from the body.
MATERIAL REQUIRED:
i) Bunsen burner
ii) Forceps
iii) Sterilised Cotton swab.
iv) Nutrient agar plates.
v) Alcohol.
PROCEDURE:
i) Muller Hintons Agar(MHA) media was taken.
ii) Cotton swab was dipped in an organism containing a test tube and swabbed on the surface of MHA agar.
iii) Four antibiotic discs were placed 2 cm far apart from each other and at a distance of 15mm from the corner of the agar plate with the help of the sterile for cep and pressed lightly to each antifiated disc.
iv) The agar plate was then incubated at 37°c for 24 hours.
v) The zone of inhibition was noted and measured with the help of a millimetre ruler.
vi) The measured zones of inhibition were compared with the AST chart.
OBSERVATION TABLE:
| S.N. | Media | Antibiotic | Organism Zone of resistance size(mm) | E.coli Susceptibility mm) |
| 1. | Muller hinton agar (MHA) | I) Nitrofurantoinii) Gentamiciniii) Ampicilliniv) Norfloxacin | 1212 | 1517 |
RESULT AND CONCLUSION:
Zone of resistance and susceptibility of E. coli for respective antibiotics was found according to the above -mentioned table. The zone of resistance was formed due to the diffusion property of antimicrobe into the medium and due to the growth of microorganisms.
The zone of susceptibility were due to the property of drug to prevent the bacteria to grow in the medium the efficiency of a drug can be determined by the measurement of the zone of susceptibility.
CONCLUSION:
The antimicrobial susceptibility test is helpful to determine the efficiency of drug toward their respective organisms.
PRECAUTION:
i) While pressing the disc, the disc should not be pressed inside the agar.
ii) The disc should have paper inoculum.
iii) The agar plate should be incubated in the right position.
REFERENCE:
Shah P.K, Dahal P.R. Amatya I (2013). “Techniques in Microbiology” Heritage Publisher and Distributor, Bhotahity KTM, Nepal Page no. 153-158.

