Methyl Red Test:
Micro-organisms when grown in MR-VP or clark and lub’s medium containing a limited amount of carbohydrate ferment it to produce acids which lowers the PH of the medium. Certain genera go on producing more acids in a mixed acid fermentation making the PH of the medium too low. The basic principle of this test is to defect the ability of an organism. Large amounts of organic acids like formic acid, acetic acid, lactic acid, succinic acid as end products. From glucose, the pH of Medium lowers down to 5 or less.
Glucose + H₂o —————>Lactic acid + Acetic acid + Formic acid + Ethanol
To test if sufficient amount of acid has been produced in the culture, a pH indicator Methyl red is added to it. The indicator turns red at pH 4.4 and below and becomes yellow at PH 6.2 and above. In a positive MR-test the reagent remains red indicating the large amount of acids were produced by bacteria growing in medium. The negative reaction is orange or yellow indicating less acid production.
Material required:
i) MR/VD Medium (Methyl-Red / Voges Proskasser medium)
ii) Methyl Medium
iii) Methyl red reagent
iv) Benien hamer
v) bacterial Burner
vi) Inoculating loop
vii) Incubator
Procedure:
i) A sterilised tube containing MR/VP broth was taken.
ii) The tube was inoculated aseptically by taking growth from an 12-24 hours pure culture with the help of a sterilised inoculating loop.
iii) Then, the tube was incubated at 350°s for 48 hours.
iv) After incubation, methyl red indicator was added directly to the incubated tube of each set.
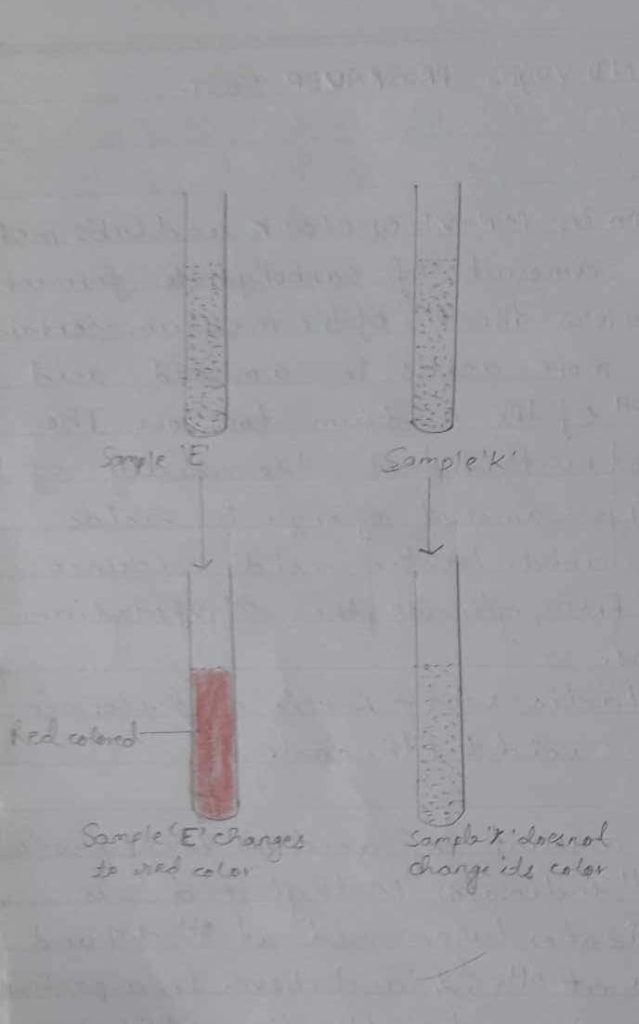
v) Finally a change in colour of methyl red was observed.
Observation Table
| Media Used | Rengest Used | Colour Observed | Result | Remarks |
| Methyl red/voges proskauer broth | Methyl red | red | Methyl red positive | Methyl red +ve bacteria was observed |
Result:
The given Sample showed a positive methyl red test.
Discussion:
The methyl red determines whether micro-organisms perform mixed acid fermentation when glucose is supplied. The provided sample showed a positive MR test as red colour appeared after the addition of methyl red reagent.
Hence,a methyl red test of an organism was performed.
Precautions:
i) The tube must be labelled property.
ii) Equipment should be carried out in sceptical conditions.
Voges-Proskauer Test:
Mast micro-organisms MR-VP medium initially convert some dextrose to acids. Then certain genera follow mixed acid fermentation pathway and produce more stable acids while -Some further metabolise the acids to less acidic end products such as 2,3-butanediol. The Voges-Proskauer Test is used to detect the ability. Reagents used in thisted don’t actually identify 2,3-butanediol but rather identify its precursor actional (acetyl methyl carbinol) Since these two substances are always found together, the presence of one is a reliable indicator for the presence of another. After appropriate incubation, Bartt’s reagent A (α- Naphthol) and B(KOH) are added to the sample. The tube is gently shaken to aerate the medium and oxidize acetoin diacetyl further reacts with components of the pepton (nitrogenous compound called guanidine nuclei) under alkaline condition to form a red colour which indicates positive vp test.
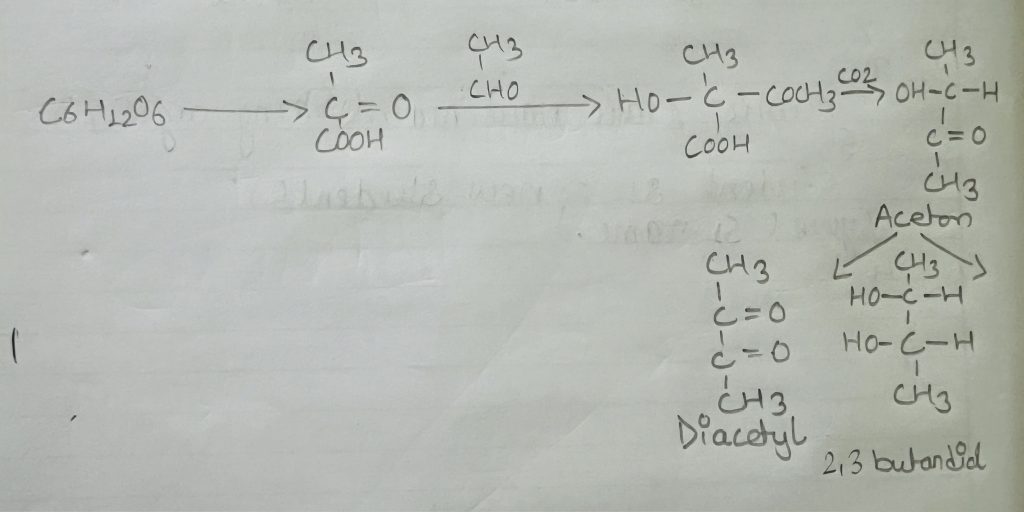
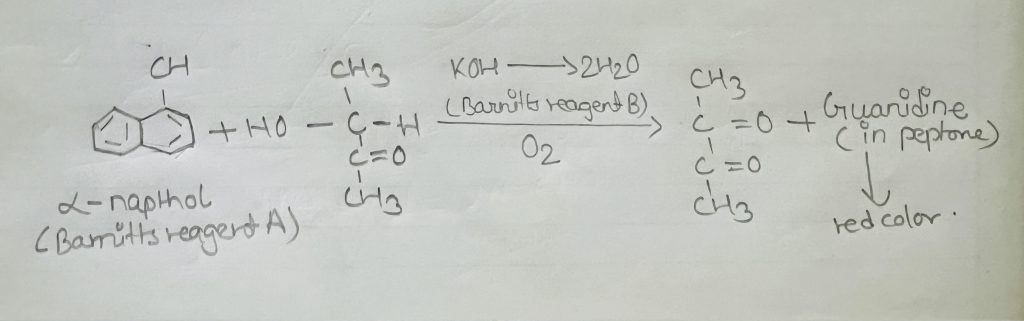
Materials Required:
i) MR-VP broth (Methyl-Red / Voges – Proskauer broth)
ii)Barrit’s reagent A
iii) Barrit’s reagent B
iv) Bacterial Suspension
v) Inoculating Loop
vi) Bunsen Burner.
Procedure:
i) A sterilised tube containing MR-VP broth((methyl red-voges-proskauer) was taken.
ii) The tube was inoculated from the growth of an 18-24 hours pure culture with the help of an inoculating loop.
iii) Then, the tube was Incubated at 35°C for 24-48 hours.
iv) After incubation about 0.6 ml of a 5% 2-naphthol solution was taken and added to the tube..
v) Then about 0.2 ml of 40% KOH-solution was added to the above tube.
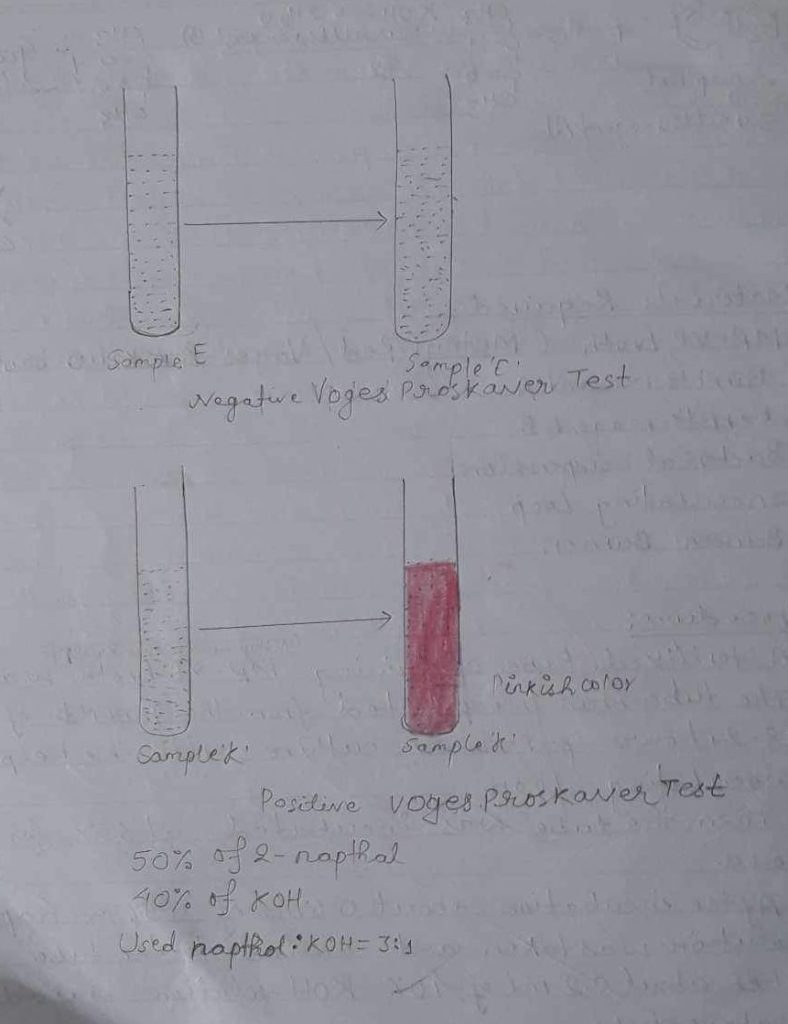
vi) The tube was gently shaken to expose medium to atmospheric oxygen in order to oxidise acetate so as to obtain a colour reaction.
vii) Finally, the tube was allowed to stand at least 10-15 minutes for observation.
Observation:
| Media Used | Reagent Used | Colour observed | Result | Remarks |
| MethylRed / Vogesproskauer broth | α- naphthol KOH | Pinkish colour | Voges proskauer positive | Positive bacteria was observed |
Result:
The given sample showed a positive Voges Proskamer test.
Discussion:
Voges Proskamer a test used to detect acetone in a bacterial broth culture. This text depends on the digestion of glucose to acetyl methyl carbinol. Hence, the provided sample showed positive VP-test by showing pinkish red color
Conclusion:
Hence, the Voges-Proskauer test of the organism was performed with above procedure.
Precautions:
i) The tubes should be labelled properly.
ii) Experiment should be out in a sceptical condition.
References:
“Manandhar S; Sharma S; (2013) “Practical Approach to microbiology” Revised edition, National book centre. Page 72-74.
